
National Digital Health Mission Harnessing Technology To Strengthen Healthcare In India
CIOReviewIndia Team | Tuesday, 01 September 2020, 09:31 IST
 During the 74th Independence Day speech, Hon’ble Prime Minister, Shri Narendra Modi declared an important healthcare scheme for the country. The Prime Minister said that the National Digital Health Mission (NDHM), prepared by the Ministry of Health Family Welfare (MoHFW) panel based on the National Digital Health Blueprint (NHDB) will construct a framework for the National Health Stack (NHS), which was proposed in 2018 by the National Institution for Transformation of India (NITI) Aayog. NHS is majorly a set of core building blocks for building as a common public good, which helps in avoiding of efforts and achieves convergence in the IT systems of the diverse stakeholders like Governments, the Payers and the Providers and the Citizens.
During the 74th Independence Day speech, Hon’ble Prime Minister, Shri Narendra Modi declared an important healthcare scheme for the country. The Prime Minister said that the National Digital Health Mission (NDHM), prepared by the Ministry of Health Family Welfare (MoHFW) panel based on the National Digital Health Blueprint (NHDB) will construct a framework for the National Health Stack (NHS), which was proposed in 2018 by the National Institution for Transformation of India (NITI) Aayog. NHS is majorly a set of core building blocks for building as a common public good, which helps in avoiding of efforts and achieves convergence in the IT systems of the diverse stakeholders like Governments, the Payers and the Providers and the Citizens.
Improving efficiency, transparency and effectiveness noticeably, the NDHM will guide the health service delivery and play a major role in stepping towards achieving United Nations Sustainable Development Goal 3.8 of the Universal Health Coverage, which includes financial risk protection.
NDHM’s mission includes developing the backbone which is utmost for supporting the integrated digital health infrastructure of India. Using digital highways, it will bridge the existing gap lying between different stakeholders of the healthcare industry.
NHDM’s Scope
Developing, designing, and implementing core and the common digital building blocks is what NDHM is aimed at for guaranteeing the essential in healthcare. It will be available to the public and the private ecosystem in cloud-based services. The services will ensure one key capability in the multiple health services, giving access through simple and open Application Interfaces (APIs).
The digital mission aims at creating some core digital systems for supporting on-time access to safe, affordable healthcare solutions to all citizens and also accelerating the country’s progress in the Universal Health Coverage (UHC). The solution consists Health ID, DigiDoctor, Health Facility Registry (HFR), Personal Health Records, e-pharmacy and telemedicine. It is comparable to the other healthcare programs of the Government, and NDHM is supposed to give these in phases.
- Health ID – It will be useful in identifying and authentication of people, read their health records and give post consents in multiple systems and stakeholders.
- DigiDoctor – In one single repository of every doctor details will be present including name, qualification, name of the institution from which a doctor graduated, specialization, registration number with the respective state medical councils, years of experience, and others. Doctors will have free digital signature, through which it can prescribe medicines to patients.
- HFR – It is Health Facility Registry, a single repository of all health facilities in the country, which will be used for storing and promoting exchange of standardized data from public and private health facilities in India and it will be maintained centrally. HFR will ensure health facilities to create and update their profiles. Health facilities will be able to e-sign documents like patient records and apply for empanelment.
- Personal Health Records – It is an electronic record for maintaining health information, which relates to nationally recognized interoperability standards, will be able to extract a record from multiple sources while it is being managed or shared or controlled by any individual. It is not like EHR or EMR as the information controlling power stays with the individual.
NHDB has structured the technology and given separate arms for management and governance. Government arm will have regulation power and the other arm will be managing the operations and implementations.
The Hierarchy Will Be As Follows –
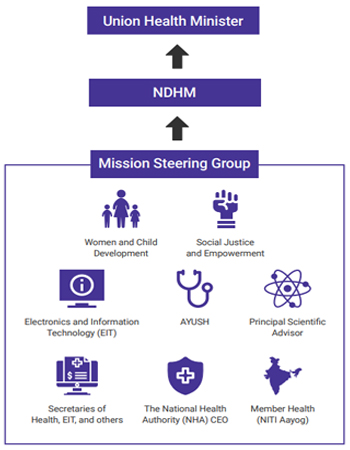
The Finance Ministry has already approved the initial budget of Rs. 470 crore for the session of 20-21. The pilot launch of the mission was approved by the Prime Minister on the Independence Day for the regions of union territories of Chandigarh, Ladakh, Dadra and Nagar Haveli, Daman and Diu, Puducherry, Andaman and Nicobar Islands, and Lakshadweep. There will be close monitoring of the pilot program and based on the reports, the countrywide implementation will take place.
The Key Features Include:
NDHM’s mission is popular among the stakeholders as:
- Individual Data Owner – Sharing an individual’s health record will require consent from him/her. The data will be available at the hospital servers in a federate architecture. Even the Government will require consent for sharing data.
- Voluntary Participation – It’s a voluntary participation enrolment process. The benefits offered is likely to encourage participation.
- Privatization – Though it is created by the government, yet private players are welcome to suggest solutions, thereby abolishing duplication chances and increasing efficiency.
- Design – The technology will be designed to make the systems interoperable with the individual hospitals and enhance data communication.
This latest technology for creating a strong healthcare system in India is a big step towards saving a life in an emergency, and normal conditions, as at times it becomes difficult for doctors to collect a requisite datum when required. The other side involves where data of healthcare systems will be available and it is much beneficial for the treatment availing parties to know how to proceed.
CIO Viewpoint
Integrating New Technologies to Optimize...
By Abhrasnata Das
Quantum Shift in Healthcare Driven by...
By Abhrasnata Das
Product Adoption: Realizing The Real Value
By Ashish Pandey, CIO, GSK Consumer Healthcare India
CXO Insights
HIT Promotional Products: Fostering Empowerment...
By Eric Shonebarger, President & Lori Thibado, Director of Order Entry & Art
Addressing the Data Management Challenges in...
By Richa Singh
Elevating Patient Experience with Remote...


















